Try Falco on Ubuntu
0. Requirements
0.1 Environment
This scenario has been tested on an Ubuntu 20.04 Virtual Machine.
To use the same specifications, you can use the following Vagrantfile:
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
# Ubuntu 20.04
config.vm.box = "bento/ubuntu-20.04"
config.vm.box_version = "202303.13.0"
# Falcosidekick-UI Dashboard HTTP Access
config.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 2802, host: 2802
end
1. Installing Falco
These are the main steps to install Falco on Ubuntu. Follow them and you should be able to use Falco in a matter of minutes.
1.1 Set up the package repository
Add Falco repository key to allow the package verification when installing it.
curl -fsSL https://falco.org/repo/falcosecurity-packages.asc | \
sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/falco-archive-keyring.gpg
Add Falco repository. This is where Falco package is located.
sudo cat >/etc/apt/sources.list.d/falcosecurity.list <<EOF
deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/falco-archive-keyring.gpg] https://download.falco.org/packages/deb stable main
EOF
Read the repository contents
sudo apt-get update -y
1.2 Install kernel headers
Kernel headers are required to compile the Falco driver. Run the following command to install them:
sudo apt-get install -y dkms make linux-headers-$(uname -r)
This step might not even be necessary if the specific driver for the Linux kernel in your host is prebuilt and offered by Falco.
1.3 Install the package dialog
The package dialog is required by Falco to be able to select at installation time which driver Falco will use.
sudo apt-get install -y dialog
1.4 Install the package falco and its dependencies
Install the latest version of the Falco package:
sudo apt-get install -y falco
Dependencies are automatically included. The total installation time will depend on the current state of the server.
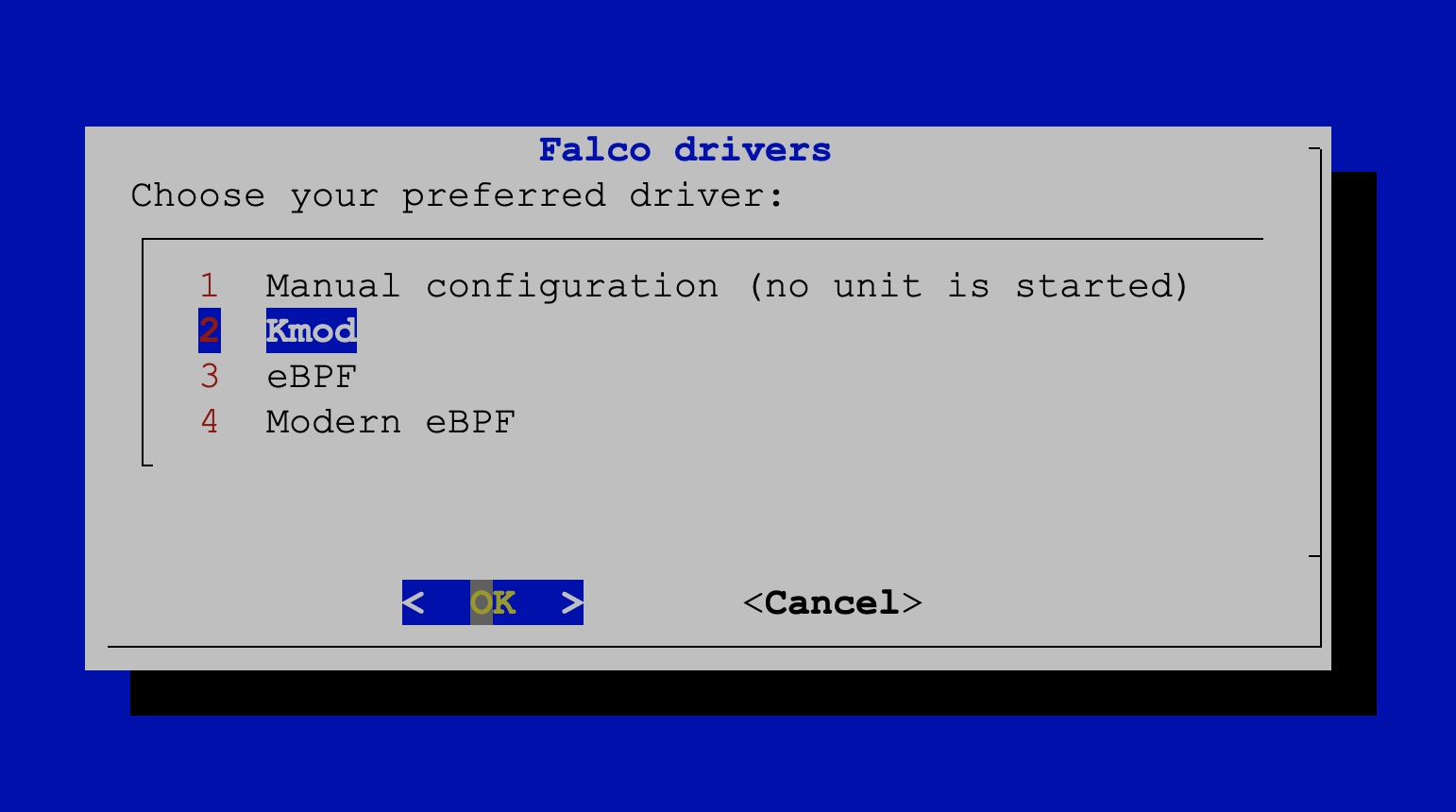
Choose the Kmod option. This will compile the Falco module for your specific kernel version.
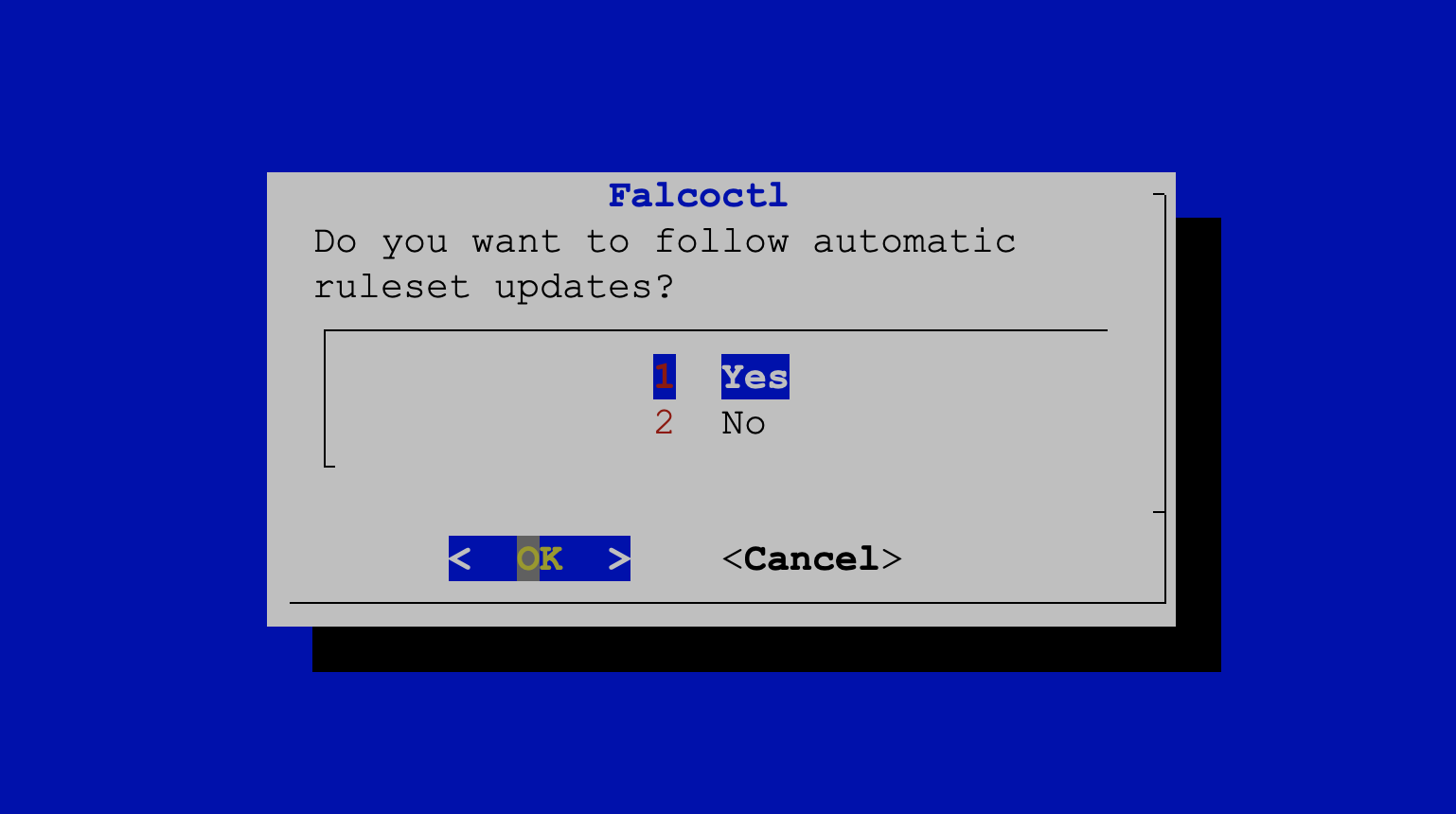
Choose the first option here. Although we won't work with it on this scenario, it will allow Falco to update its rules automatically.
After some seconds, if everything went as expected, Falco will be enabled and running. The quickest way to verify this is executing the following command:
sudo systemctl is-active falco
active
If you see that the output is different, you might need to start it manually:
sudo systemctl start falco
1.5 Verify the Falco installation
To verify that Falco is running correctly and obtain more detailed information about the service, use the following systemctl command:
sudo systemctl status falco
The output should look like the following with the green color:
● falco-kmod.service - Falco: Container Native Runtime Security
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/falco-kmod.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Wed 2023-01-25 10:44:04 UTC; 12s ago
Docs: https://falco.org/docs/
Main PID: 26488 (falco)
Tasks: 9 (limit: 2339)
Memory: 13.1M
CGroup: /system.slice/falco-kmod.service
└─26488 /usr/bin/falco --pidfile=/var/run/falco.pid
Jan 25 10:44:04 ubuntu systemd[1]: Started Falco: Container Native Runtime Security with kmod.
Jan 25 10:44:04 ubuntu falco[26488]: Falco version: 0.34.1 (x86_64)
Jan 25 10:44:04 ubuntu falco[26488]: Falco initialized with configuration file: /etc/falco/falco.yaml
Jan 25 10:44:04 ubuntu falco[26488]: Loading rules from file /etc/falco/falco_rules.yaml
Jan 25 10:44:04 ubuntu falco[26488]: Loading rules from file /etc/falco/falco_rules.local.yaml
Jan 25 10:44:04 ubuntu falco[26488]: The chosen syscall buffer dimension is: 8388608 bytes (8 MBs)
Jan 25 10:44:04 ubuntu falco[26488]: Starting health webserver with threadiness 2, listening on port 8765
Jan 25 10:44:04 ubuntu falco[26488]: Enabled event sources: syscall
Jan 25 10:44:04 ubuntu falco[26488]: Opening capture with Kernel module
Notice that, despite interacting with the
falco.serviceunit, it showsfalco-kmod.servicestatus and also the logs.
2. Trying Falco in action
2.1 Generate a suspicious event
Run the following command to simulate a suspicious event:
sudo cat /etc/shadow > /dev/null
2.2 Look at Falco logs
There are different ways to access Falco logs in this installation:
2.2.1 Via journalctl
jounalctl allows us to interact with journald to inspect our services. Run the following command to retrieve Falco messages that have been generated with a priority of warning:
sudo journalctl _COMM=falco -p warning
...
Jan 25 10:52:54 ubuntu falco: 10:52:54.144872253: Warning Sensitive file opened for
reading by non-trusted program (user=root user_loginuid=-1 program=cat command=cat
/etc/shadow pid=27550 file=/etc/shadow parent=bash gparent=kc-terminal ggparent=bash
gggparent=systemd container_id=host image=<NA>)
...
2.2.2 Via /var/log/syslog
Log messages describing Falco's activity are logged to syslog. Run the following command to retrieve Falco logs:
sudo grep falco /var/log/syslog
...
Jan 25 10:52:54 ubuntu falco: 10:52:54.144872253: Warning Sensitive file opened for
reading by non-trusted program (user=root user_loginuid=-1 program=cat command=cat
/etc/shadow pid=27550 file=/etc/shadow parent=bash gparent=kc-terminal ggparent=bash
gggparent=systemd container_id=host image=<NA>)
Congratulations, you finished this scenario!
You should be able to install Falco on your Ubuntu host and watch for suspicious behavior.
Click on Try Falco and try out the next scenario.
Was this page helpful?
Let us know! You feedback will help us to improve the content and to stay in touch with our users.
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.